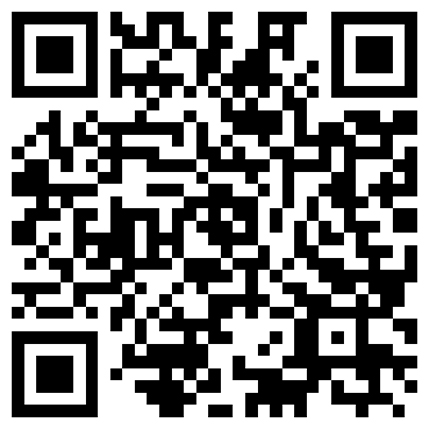


What is T-buty?
Triglyceride is produced by esterification reaction of butyric acid and glycerol in a certain proportion under acidic catalyst. Butyric acid can supply mucosal cells with energy, enable intestinal mucosal cells to proliferate and differentiate rapidly, repair damaged and aging mucosal cells, inhibit intestinal harmful bacteria, and promote the absorption and utilization of nutrients.
Characteristics
 | The high-content liquid raw material T-buty95 offers a 30% reduction in the required amount compared to powdered formulations available on the market, resulting in significant cost savings for feed mills. Additionally, this raw material provides a price advantage, making it an ideal choice for feed mills aiming to improve cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency. |
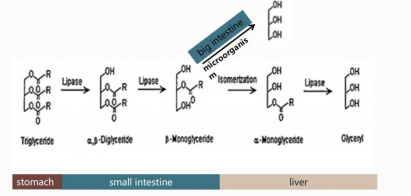
 | Tributyrin undergoes a similar digestive process in animals to that of lipids, so it is only slightly broken down in the stomach. In the intestines, tributyrin is hydrolyzed into glycerol monoester and two butyric acids by pancreatic lipase. The butyric acids are rapidly absorbed by the small intestine and enter the bloodstream. Compared to sodium butyrate, tributyrin can reduce the consumption of stomach acid and improve the utilization of butyric acid. |
 | The liquid raw material T-buty95 can be directly mixed with fats or formic acid in feed, and then sprayed onto the feed surface through the system, making it easier to operate and ensuring more even distribution. |
Effect
1.It provides rapid energy for intestinal mucosal cells, and is evenly absorbed in the foregut, midgut, and hindgut,effectively repairing damaged mucosa, preventing nutritional diarrhea in colon and proliferative ileitis.
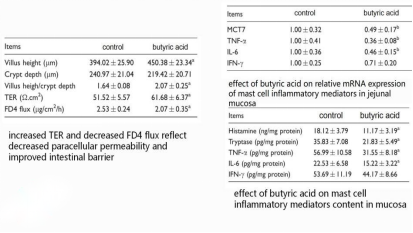
2.Regulate the intestinal microflora, promote the growth of beneficial bacteria; inhibit harmful bacteria, and have an inhibitory effect on Salmonella, E. coli, etc.

3.Improve the growth performance of animals, promote feed intake, and reduce the F/G.


